EXCELLENCE IN OPERATIONS
The “Functional Excellence in Implementation” ensures that we translate the complex task into operational measures and transfer these into the target state highly effectively applying appropriate methods and tools with the resources available.
The sub-strategies of the respective functional areas are worked out based on the vision and strategy work. In the course of this process, it becomes clear which functional area must be provided with which profit contribution for the transformation. The challenge in the operational implementation lies in defining THE measures which deliver significant profit contributions compared with the resources used with the aid of a careful selection of methods and tools.
A key success factor to achieving this effectiveness lies above all in understanding how the respective functional areas considered by themselves can be transferred into a “functional excellence” or by which methods and tools an organisational unit becomes the “benchmark”.
The prerequisite for this is that one is familiar with the most critical and effective methods and tools in order to use the right tool from this present toolbox at the right moment. Success ultimately lies in being very restrictive in the number of methods and tools selected (in the sense of “less is more”) and thereby being very consistent in their application and implementation.
Use of world-leading production systems.
We have already been operating in the business of the international manufacturing industry for decades and know all the conventional and modern methods and tools in order to attain the “functional excellence” of a business unit. We are aware of world leading production systems such as the TPS (Toyota Production System) and the BPS (Bosch Production System) and use these.
We are aware of the “toolbox” and provide this.
WE ARE PARTNERS IN THE KEY TOPIC AREAS OF EXCELLENCE
Extract:
STRIVING FOR
QUALITY LEADERSHIP
in the respective market and product segment; treading the path of a “zero-defect strategy” (in particular for safety-related products); knowledge regarding the introduction and implementation of certifications, such as IATF 16949
STRIVING FOR
COST LEADERSHIP
through the use of the latest methods and tools for enhanced efficiency
DEVISING
PRODUCTION AND
ADDED-VALUE STRATEGIES
at a time of digitisation and under the influence of the “Internet of Things and Services” and “Industry 4.0”
TAILORING
INTERNATIONAL
SITE STRATEGIES
to the market and cost situation of the company
DIMENSIONING
INTERNATIONAL PRODUCTION NETWORKS
and bringing these to a high operating performance through collaboration. In conjunction with a design whereby structures and business processes in the international network can be kept very streamlined. The selected approach guaranteeing a high completely entrepreneurial level of efficiency through the use of synergies
DERIVING
TARGET STRUCTURES
for the respective sites and divisions from the strategy-identification process, dimensioning these and implementing them jointly with the people on site
ADAPTING AND CREATING
BUSINESS PROCESSES
in line with requirements
LEADING AND IMPLEMENTING
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
AND SE-WORK
(Simultaneous Engineering) throughout the product development process effectively for the customer
(> The Project Management Office)
Companies which have to deliver a greater change service are, generally speaking, firstly confronted with working out and implementing this need for transformation and secondly ensuring that the day-to-day business is fully delivered and handled for the customer without any restrictions.
We can play a part in the company during this transformation phase by temporarily safeguarding this growing demand for resources (capacity) and skills with our specialists and our network.
DIGITISATION
THE DIGITISATION STRATEGY
IS PART OF THE STRATEGIC RESTRUCTURING
AND IS PART OF THE CORPORATE STRATEGY
Key “technological revolutions” are being driven by the advent and rapid development of digitisation.
Understanding the development process of growing global interconnectedness and digitisation will empower companies to further refine their existing unique selling points and work out new distinguishing features in a competitive environment. The use of “IIoT” data forms a key basis for this.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) – Industry 4.0
In particular, the “industrialised” application of the “Internet of Things” (IIoT) will change the market and competitive landscape significantly and sustainably. The activities of the IIoT are thereby part of a holistic course of action to enhancing and safeguarding competitiveness towards a market dominance of products and services.
We can shape the relevant business processes and business segments in your company by assessing and incorporating the use of options via digitisation and Industry 4.0.
We can provide a technology network which covers the other areas of digitisation (incl. ERP, security, big data, data analytics, the Cloud, sensor technology).
We can guide you from the idea to its implementation on site and integrate your customers and staff into the digital transformation process.
CONDUCTING DIGITISATION CHECK
Digital transformation is an ongoing process and it must be explained from the corporate governance to the management issue. Digitisation requires a targeted, long-term oriented course of action with an overall approach to realise quick wins.
We can shape the future together with you by addressing challenges, pointing out opportunities and tackling these pragmatically in order to attain fast and measurable results.
Actively plan and manage the digital transformation in your company with us
The positioning of a company is performed in the digitisation. To establish the ACTUAL situation, ongoing activities are recorded for the digitisation and are subjected to an initial assessment. In doing this, we consider, amongst other things, examples of ongoing projects (e.g. projects regarding Industry 4.0, efficiency and process optimisations, IT projects). The internal company skills and aptitudes are recorded as well as the perspective of the customer.
STRATEGIC ACTION AREAS
CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE
Customer requirements and expectations are worked out (e.g. prices, product features, ease of use, communication channels and technologies with the customer, service, etc.).
DIGITAL PRODUCTS
AND SERVICES
Products and services are derived from future market developments and are assessed in comparison with the competition. Future digital business models, digital product models and functions and digital services are described.
DIGITAL ORGANISATION,
PROCESSES AND
INDUSTRIALISATION
Corporate challenges stem from the customer expectations, products and services to be realised and are translated into appropriate digitisation requirements for subsequent realisation (e.g. product variance, complexity, flexibility, efficiency, levels of automation, networking of the value-added and logistical processes, data provision (big data), qualifications of staff, etc.).
- This approach should provide clarity regarding what digital transformation is needed as regards customer requirements, products & services and organisation incl. industrialisation and logistics.
IMPLEMENTING
DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION
Together with the staff, we devise a transformation strategy tailored to the company. Action areas, potentials and feasibility are worked out and assessed with representatives from the company’s IT (and IT Security) departments and staff, who come from the fields of application. Specific transformation measures are defined and their implementability is also assessed with regard to the corporate culture and staff qualifications.
Feasible solutions and quick wins in implementing digitisation
Success factors for a successful digitisation transformation include early integration of the staff, combined with further consistent training. It is extremely important that people can see the pragmatism of the approach selected. The cost / benefit effect must be clearly understood and, in conjunction with quick wins, the prerequisites of a motivation for change emerge. The people must fully experience the benefits of the measures introduced for digitisation.
Making digital transformation perceptible.
Experience digitisation in the language of the staff from the respective divisions and define the action areas.
ACTION AREAS OF THE IMPLEMENTATION
BUSINESS MODELS
NEW PRODUCTS
AND SERVICES
ENHANCING EFFICIENCY
- Screening of the existing business processes and working out the potential for optimisation.
- Transferring new business and service models into the day-to-day business using new processes.
BUSINESS MODELS / NEW PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
Examples:
How the company can create new business areas and business models by means of digitised products and services is considered here, for example. Just as additional added value in the company can be generated by the digitised approach.
Another aspect lies in the creation of transparency regarding products in the lifecycle/ product use sector, which very often opens up completely new opportunities. The introduction of new service models enables new differentiations to the competition to be worked out and opens up new revenue streams.
ENCHANCING EFFICIENCY
The North Star:
The material flows and is constantly in motion.
The capital intensive machinery and equipment run without interruption.
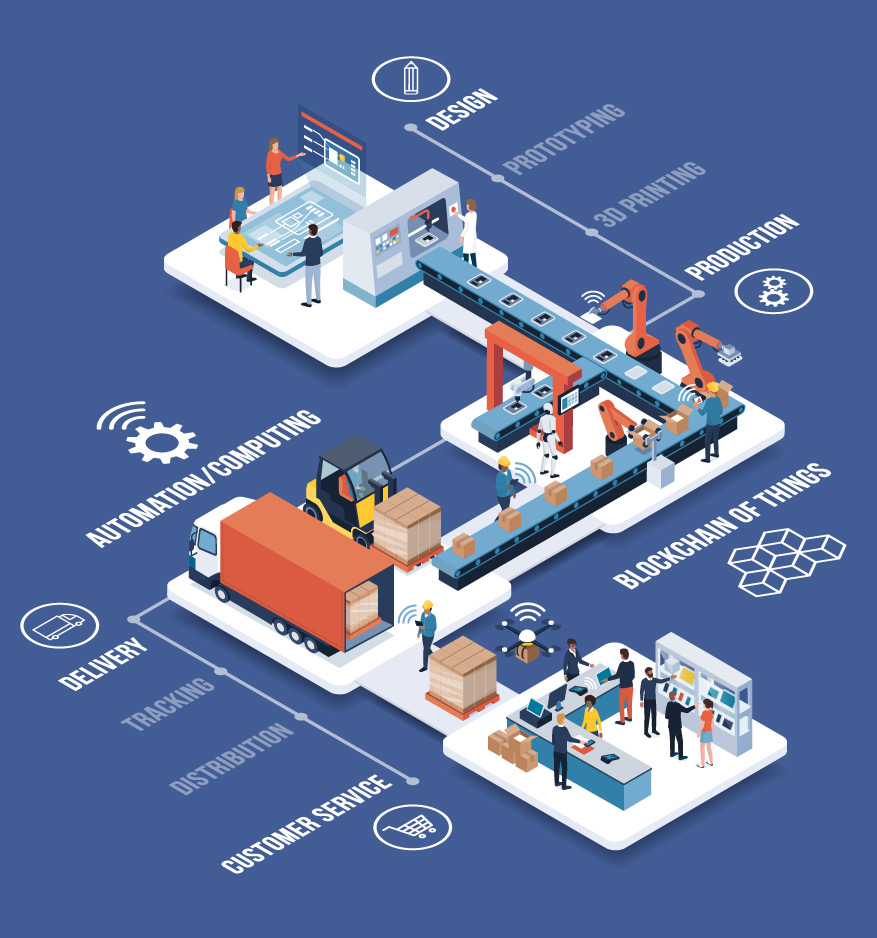
In the smart factory, all the resources and process elements in the value-added chain of logistics and production are linked together. They communicate and operate in constant coordination with all the upstream and downstream processes within the network. The conventional sequential value-added chain develops towards an automated value-added network.
The sequential value-added chain becomes the automated value-added network.
Examples:
SUPPLY CHAIN
Motivation:
Reduce shipment costs
The number of shipments is significantly reduced; the cargo carriers have a high capacity.
Approach: Transport efficiency and the capacity of cargo carriers increase due to routes being more dynamic
Lead and throughput times
Lead and throughput times are significantly reduced. There is a high delivery reliability in terms of time. Work-in-process assets and capital commitment are significantly reduced.
Approach: Close interlinking of logistical processes (supplier, shipment, plant entrance) with value-added processes (production) and mapping the flow of goods in real time. Establishing the data exchange along the supply chain across all processing steps involved.
Inventory reduction in the plant:
There are no material stocks, but the material migrates into a “flowing state”.
Approach: Speeding up the processes in the receiving and delivery department (ramp). Introduction of efficient intralogistics processes (outflow/inflow of goods) in the production department in conjunction with incoming and outgoing goods.
PRODUCTION
Motivation:
Maximising utilisation level of machinery and equipment.
Avoid production shutdowns in conjunction with maximum capacity utilisation of the investment available.
Approach: The real production situation is in line with the planning. Indications regarding maintenance and servicing are handled in real time.
Maximising technical availability of machinery and equipment.
Sophisticated preventative maintenance and servicing systems increase the utilisation and reliability of existing production capacities and, at the same time, optimise the costs of the maintenance of complex machinery and equipment.
Approach: Predict technical faults and take action before the fault occurs.
Digitisation and SAP
We exploit untapped potential with the aid of digitisation.
Our SAP specialists support companies in their SAP system landscape with the digital transformation and optimisation of processes. We work through connections and synergies together, then use and integrate them. This takes into account the further development of the SAP system landscape in the coming years.